Abstract
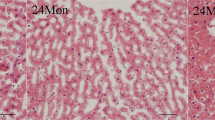
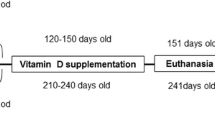
In aging liver oxidative stress increases due to the decrease in antioxidant bio-molecules such as estrogens which can be modified by hormonal replacement therapy (HRT). With this in mind, we hypothesized that age-related decline in steroidogenesis may be associated with the impairment of the antioxidant defense cells in liver, the increase in lipid peroxidation, hepatic dysfunction and histological changes; estrogens prevent all these changes induced by aging. 17β-estradiol treatment was initiated in 12 month-old Wistar rats, and continued until 18 months of age. Our results showed that 17β-estradiol (E2) level in the serum of the aged untreated rats was reduced by −32% in 18 month-old rats compared to the young animals (4-month-old). The superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and gluthatione peroxidase (GPX) activities were reduced by −47, −46, and −29% respectively in old rat liver. In addition, the TBARs in liver and hepatic dysfunction parameters in plasma such as gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), phosphatase alkalin (PAL) as well as bilirubin level increased significantly in old rats, and histological changes were investigated. In E2-treated rats, protective effects were observed. Indeed, 17β-estradiol attenuates all changes induced by aging. The 17β-estradiol level was higher in old E2-treated rats compared to the control rats. Moreover, the SOD, CAT and GPX activities were higher by +28, +15, and +11% respectively. This anti-aging effect of estrogens was clarified by a lower level of lipid peroxidation and liver dysfunction parameters as well as by histological observation.
Resumen
El estrés oxidativo hepático aumenta con el envejecimiento debido a la disminución de moléculas antioxidantes como los estrógenos, lo que puede ser modificado mediante tratamiento hormonal sustitutorio. Se estudia en este trabajo el efecto del tratamiento a largo plazo con 17β-estradiol (E2) sobre los cambios asociados al envejecimiento hepático. El tratamiento con E2 se inició en ratas de 12 meses y continuó hasta los 18 meses. Los resultados mostraron un descenso del 32% del nivel sérico de E2 en ratas no tratadas respecto de los animales jóvenes (4 meses). La actividad superóxido dismutasa (SOD), catalasa (CAT) y glutatión peroxidasa (GPX) se redujo el 47, 46 y 29% respectivamente en hígado de ratas viejas. En elmismo sentido, aumentaron significativamente parámetros séricos indicativos de disfunción hepática, como la actividad gammaglutamil transferasa, fosfatasa alcalina y el nivel de bilirrubina. El tratamiento con estradiol incrementa la actividad SOD, CAT y GPX y disminuye el nivel de peroxidación lipídica y los parámetros indicativos de disfunción hepática. Los resultados indican que el E2 puede mejorar la disfunción hepática asociada al envejecimiento en ratas macho viejas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi, H. (1984): Methods Enzymol., 105, 121–126.
Baquer, N.Z., Sochor, M., Kunjara, S., McLean, P. (1993): Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int., 31, 509–519.
Borras, C., Gambini, J., Gómez-Cabrera, M.C., Sastre, J., Pallardo, F.V., Mann, G.E., Vina, J. (2005): Aging cell, 4, 113–118.
Borras, C., Sastre, J., Garcia-Sala, D., Lloret, A., Pallardo, F.V., Vina, J. (2003): Free Radic. Biol. Med., 34, 546–552.
Buege, J.A., Aust, S.D. (1984): Methods Enzymol., 105, 302–310
Cadenas, E., Davies, K.J. (2000): Free Radic. Biol. Med., 29, 222–230.
Dizdaroglu, M., Jaruga, P., Birincioglu, M., Rodríguez, H. (2002): Free Radic. Biol. Med., 32, 1102–1115.
Dröge, W. (2002): Physiol. Rev., 82, 47–95.
Finkel, T., Holbrook, N.J. (2000): Nature, 408, 239–247.
Garret, H.E. (1956): Elementary statistics. Now York: Longmans Green and Company.
Genissel, C., Carreau, S. (2001): Mol. Cell Endocrinol., 178, 141–146.
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R.J. (1951): J. Biol. Chem., 193, 265–275.
Marklund, S., Marklund, G. (1975): Eur. J. Biochem., 47, 469–474
Mikkola, T.S., Clarkson, T.B. (2002): Cardiovasc. Res., 53, 605–619.
Moorthy, K.D., Sharma, S.F., Basir, Baquer, N.Z. (2005): Exp. Gerontol., 4, 295–302.
Nasr, A., Breckwoldt, M. (1998): Gynécol. Endocrinol., 12, 43–59.
Pagila, D.E., Valentine, W.N. (1967): J. Lab. Clin. Med., 70, 158–169.
Pinzani, M., Romanelli, R.G. and Magli S. (2001): J. Hepatol., 34, 764–767.
Prokai, L., Prokai-Tatrai, K., Perjési, P. and Simplins, J.W. (2006): Drug. Dev. Res., 66, 118–125.
Roberts, L.J. and Reckelhoff, J.F. (2001): Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 287, 254–256.
Ruiz-Larrea, M.B., Leal, A.M., Martin, C., Martínez, R. and Lacort, M. (1997): Rev. esp. Fisiol., 53, 225–229.
Squier, T.C. (2001): Exp. Gerontol., 36, 1539–1550
Sugioka, K., Shimosegawa, Y. and Nakano, M. (1987): FEBS Lett., 210, 37–39.
Valls V., Peiro C., Muñiz P. and Saez G.T. (2005): Process Biochem., 40, 903–908.
Vina, J., Borras, C., Gambini, J., Sastre, J. and Pallardo, F.V. (2005): FEBS Lett., 579, 2541–2545.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamden, K., Carreau, S., Ellouz, F. et al. Protective effect of 17β-estradiol on oxidative stress and liver dysfunction in aged male rats. J. Physiol. Biochem. 63, 195–201 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03165782
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03165782