Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the distribution of retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) and macular retinal thickness measured by optical coherence tomography (OCT) in a Thai population.
Methods
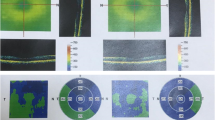
We studied one eye each of 250 healthy subjects [age ≥ 18 years; spherical refractive error within ±6 diopters (D); astigmatism ≤3 D; no ocular pathology]. A complete eye examination, standard automated perimetry, and fast RNFL and macular thickness measurement by OCT were performed, and a disc photograph was taken. The distributions of both thicknesses, including their relationship with demographic data, were analyzed.
Results
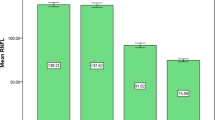
The mean ± SD age of the study population was 44.7 ± 12.2 years. The mean ± SD RNFL thickness was 109.3 ± 10.5 m, which was 10% thicker than that in the OCT normative database. RNFL decreased 2.3 m per decade (P < 0.001). Sex and spherical equivalent were not associated with RNFL thinning. The mean ± SD central foveal thickness was 183.2 ± 1.3 m. The macular thickness in the outer area was significantly thinner than that in the inner area (P < 0.001). The temporal regions were the thinnest among the four quadrants (P < 0.001). Thinning of all macular areas, except the center, was found to be associated with advancing age (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
RNFL thickness in the measured Thai population was about 10% thicker than that in the original normative database. Macular thickness and RNFL thickness in the superior and inferior quadrants decreased with advancing age.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Quigley HA, Dunkelberger GR, Green WR. Retinal ganglion cell atrophy correlated with automated perimetry in human eyes with glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol 1989;107:453–464.
Patella VM. StratusOCT: establishment of normative reference values for retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurement. Dublin, CA: Carl Zeiss Meditec; 2003.
Liu X, Ling Y, Luo R, Ge J, Zheng X. Optical coherence tomography in measuring retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normal subjects and patients with open-angle glaucoma. Chin Med J (Engl) 2001;114:524–529.
Varma R, Bazzaz S, Lai M. Optical tomography-measured retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normal Latinos. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2003;44:3369–3373.
Sony P, Sihota R, Tewari HK, Venkatesh P, Singh R. Quantification of the retinal nerve fibre layer thickness in normal Indian eyes with optical coherence tomography. Indian J Ophthalmol 2004;52:303–309.
Salchow DJ, Oleynikov YS, Chiang MF, et al. Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normal children measured with optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 2006;113:786–791.
Budenz DL, Anderson DR, Varma R, et al. Determinants of normal retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by Stratus OCT. Ophthalmology 2007;114:1046–1052.
Medeiros FA, Zangwill LM, Bowd C, Vessani RM, Susanna R Jr, Weinreb RN. Evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer, optic nerve head, and macular thickness measurements for glaucoma detection using optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol 2005;139:44–55.
Wollstein G, Ishikawa H, Wang J, Beaton SA, Schuman JS. Comparison of three optical coherence tomography scanning areas for detection of glaucomatous damage. Am J Ophthalmol 2005;139:39–43.
Wong TY, Foster PJ, Hee J, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for refractive errors in adult Chinese in Singapore. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2000;41:2486–2494.
Luo R, Ge J, Liu X, Wang M, Ling Y, Zheng X. A quantitative measurement of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness by optical coherence tomography in normal Chinese people (in Chinese). Yan Ke Xue Bao 1998;14:207–209.
Kanamori A, Nakamura M, Escano MF, Seya R, Maeda H, Negi A. Evaluation of the glaucomatous damage on retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol 2003;135:513–520.
Bourne RR, Medeiros FA, Bowd C, Jahanbakhsh K, Zangwill LM, Weinreb RN. Comparability of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurements of optical coherence tomography instruments. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2005;46:1280–1285.
Schuman JS, Hee MR, Puliafito CA, et al. Quantification of nerve fiber layer thickness in normal and glaucomatous eyes using optical coherence tomography. Arch Ophthalmol 1995;113:586–596.
Tjon-Fo-Sang MJ, de Vries J, Lemij HG. Measurement by nerve fiber analyzer of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normal subjects and patients with ocular hypertension. Am J Ophthalmol 1996;122:220–227.
Poinoosawmy D, Fontana L, Wu JX, Fitzke FW, Hitchings RA. Variation of nerve fibre layer thickness measurements with age and ethnicity by scanning laser polarimetry. Br J Ophthalmol 1997;81:350–354.
Bowd C, Zangwill LM, Blumenthal EZ, et al. Imaging of the optic disc and retinal nerve fiber layer: the effects of age, optic disc area, refractive error, and gender. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis 2002;19:197–207.
Kremmer S, Zadow T, Steuhl KP, Selbach JM. Scanning laser polarimetry in myopic and hyperopic subjects. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2004;242:489–494.
Tewari HK, Wagh VB, Sony P, Venkatesh P, Singh R. Macular thickness evaluation using the optical coherence tomography in normal Indian eyes. Indian J Ophthalmol 2004;52:199–204.
Paunescu LA, Schuman JS, Price LL, et al. Reproducibility of nerve fiber thickness, macular thickness, and optic nerve head measurements using StratusOCT. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2004;45:1716–1724.
Chan A, Duker JS, Ko TH, Fujimoto JG, Schuman JS. Normal macular thickness measurements in healthy eyes using Stratus optical coherence tomography. Arch Ophthalmol 2006;124:193–198.
Massin P, Erginay A, Haouchine B, Mehidi AB, Paques M, Gaudric A. Retinal thickness in healthy and diabetic subjects measured using optical coherence tomography mapping software. Eur J Ophthalmol 2002;12:102–108.
Wakitani Y, Sasoh M, Sugimoto M, Ito Y, Ido M, Uji Y. Macular thickness measurements in healthy subjects with different axial lengths using optical coherence tomography. Retina 2003;23:177–182.
Luo HD, Gazzard G, Fong A, et al. Myopia, axial length, and OCT characteristics of the macula in Singaporean children. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2006;47:2773–2781.
Vetrugno M, Trabucco T, Sisto D, Sborgia C. Effect of cataract surgery and foldable intraocular lens implantation on retinal nerve fiber layer as measured by scanning laser polarimetry with variable corneal compensator. Eur J Ophthalmol 2004;14:106–110.
El-Ashry M, Appaswamy S, Deokule S, Pagliarini S. The effect of phacoemulsification cataract surgery on the measurement of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness using optical coherence tomography. Curr Eye Res 2006;31:409–413.
Congdon N, Wang F, Tielsch JM. Issues in the epidemiology and population-based screening of primary angle-closure glaucoma. Surv Ophthalmol 1992;36:411–423.
Foster PJ, Johnson GJ. Glaucoma in China: how big is the problem? Br J Ophthalmol 2001;85:1277–1282.
He M, Foster PJ, Ge J, et al. Gonioscopy in adult Chinese: the Liwan Eye Study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2006;47:4772–4779.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Manassakorn, A., Chaidaroon, W., Ausayakhun, S. et al. Normative database of retinal nerve fiber layer and macular retinal thickness in a Thai population. Jpn J Ophthalmol 52, 450–456 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-008-0538-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-008-0538-6