Abstract
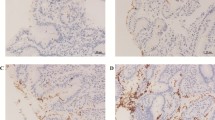
Helicobacter pylori genetic diversity and geographic distribution affect the severity of gastric histology; while eradication heals gastritis, the improvement of atrophy and intestinal metaplasia (IM) is still controversial. We investigated whether H. pylori infection and genotypes (cagA–vacA) influence the histological changes and whether eradication resolves these changes. Twenty-one patients (11 duodenal ulcer, 2 gastric ulcer, 8 gastritis) received treatment. Biopsies for CLO, PCR, histology, and culture were collected before and at 1 and 12 months after treatment, and serum samples at 0, 1, 2, 6, and 12 months. H. pylori eradication was achieved in 71% of the patients. Histological scores for H. pylori densities were significantly higher in the antrum and incisura angularis. Scores for mononuclear cell and neutrophil infiltration were significantly higher in regions with a high H. pylori density and improved progressively after eradication. Eight patients with atrophy including five with IM showed no significant changes 12 months after eradication. The cagA gene, detected in 13 (62%), the vacA-s1a gene, in 20 (95%), and the vacA-m1 gene, in 12 (57%) of 21 patients were significantly associated with duodenal ulcer. A gradual decline in antibody titer reached an average of 67% 12 months after eradication. H. pylori infection and the associated genotypes (cagA of Western type) affect the severity of the gastric histology (mild forms of atrophy and IM) and the disease outcome. Eradication of H. pyloriresulted in healing of gastritis, but with no significant improvement in atrophy or IM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sipponen P, Marshall BJ: Gastritis and gastric cancer. Western countries. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 29:579–292, 2000
Sipponen P: Natural course of Helicobacter pylori gastric infection. Ital J Gastroenterol Hepatol 30 (Suppl 3):S270–S272, 1998
Innocenti M, Thoreson AC, Ferrero RL, et al.: Helicobacter pylori-induced activation of human endothelial cells. Infect Immun 70:4581–4590, 2002
Fox JG, Wang TC: Helicobacter pylori infection: pathogenesis. Current Opin Gastroenterol 18:15–25, 2002
Kokkola A, Rautelin H, Puolakkainen P, et al.: Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with atrophic gastritis: comparison of histology, 13C-urea breath test, and serology. Scand J Gastroenterol 35:138–141, 2000
Satoh K, Kimura K, Takimoto T, et al.: A follow-up study of atrophic gastritis and intestinal metaplasia after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter 3:236–240, 1998
Ito M, Haruma K, Kamada T, et al.: Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy improves atrophic gastritis and intestinal metaplasia: a 5-year prospective study of patients with atrophic gastritis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 16:1449–1456, 2002
Ohkusa T, Fujiki K, Takashimizu I, et al.: Improvement in atrophic gastritis and intestinal metaplasia in patients in whom Helicobacter pylori was eradicated. Ann Intern Med 134:380–386, 2001
Yamada T, Miwa H, Fujino T, Hirai S, Yokoyama T, Sato N: Improvement of gastric atrophy after Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy. J Clin Gastroenterol 36:405–410, 2003
Hojo M, Miwa H, Ohkusa T, Ohkura R, Kurosawa A, Sato N: Alteration of histological gastritis after cure of Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 16:1923–1932, 2002
van der Hulst RW, van der Ende A, Dekker FW, et al.: Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on gastritis in relation to cagA: a prospective 1-year follow-up study. Gastroenterol 113:25–30, 1997
Annibale B, Di Giulio E, Caruana P, et al.: The long-term effects of cure of Helicobacter pylori infection on patients with atrophic body gastritis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 16:1723–1731, 2002
Zerbib F, Lenk C, Sawan B, et al.: Long-term effects of Helicobacter pylori eradication on gastric antral mucosa in duodenal ulcer patients. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 12:719–725, 2000
Larkin CJ, Watson P, Sloan JM, et al.: Gastric corpus atrophy following eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 13:377–382, 2001
Sharma P, Topalovski M, Mayo MS, Sampliner RE, Weston AP: Helicobacter pylori eradication dramatically improves inflammation in the gastric cardia. Am J Gastroenterol 95:3107–3111, 2000
Covacci A, Telford JL, Giudice GD, Parsonnet J, Rappouoli R: Helicobacter pylori virulence and genetic geography. Science 284:1328–1333, 1999
Yamaoka Y, Kodama T, Gutierrez O, Kim JG, Kashima K, Graham DY: Relationship between Helicobacter pylori iceA, cagA, and vacA status and clinical outcome: studies in four different countries. J Clin Microbiol 37:2274–2279, 1999
Blaser MJ, Berg DE: Helicobacter pylori genetic diversity and risk of human disease. J Clin Invest 107:767–773, 2001
Rudi J, Kolb C, Maiwald M, et al.: Diversity of Helicobacter pylori vacA and cagA genes and relationship to VacA and CagA protein expression, cytotoxin production, and associated diseases. J Clin Microbiol 36:944–948, 1997
lto V, Azume T, lto S, et al.: Analysis and typing of the vacA gene from cagA-positive strains of Helicobacter pylori isolated in Japan. J Clin Microbiol 35:1710–1714, 1997
Dixon MF, Genta RM, Yardley JH, et al.: Classification and grading of gastritis. The updated Sydney System. Am J Surg Pathol 20:1161–1181, 1996
Abasiyanik M, Sander E, Salih BA: Helicobacter pylori anti-cagA antibodies: Prevalence in symptomatic and asymptomatic subjects in Turkey. Can J Gastroenterol 16:1–6, 2002
Tham KT, Peek RM Jr, Atherton JC, et al.: Helicobacter pylori genotypes, host factors, and gastric mucosal histopathology in peptic ulcer disease. Hum Pathol 2001;32:264–273, 2001
Camorlinga-Ponce M, Aviles-Jimenez F, Cabrera L, et al.: Intensity of inflammation, density of colonization and interleukin-8 response in the gastric mucosa of children infected with Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter 2003;8:554–560, 2003
Chen XY, van Der Hulst RW, Shi Y, et al.: Comparison of precancerous conditions: atrophy and intestinal metaplasia in Helicobacter pylori gastritis among Chinese and Dutch patients. J Clin Pathol 54:367–370, 2001
Xia HH-X, Kalantar JS, Talley NJ, et al.: Antral-type mucosa in the gastric incisura, body, and fundus (antralization): a link between Helicobacter pylori infection and intestinal metaplasia? Am J Gastroenterol 95:114–121, 2000
Scholte GH, van Doorn LJ, Cats A, et al. Genotyping of Helicobacter pylori in paraffin-embedded gastric biopsy specimens: relation to histological parameters and effects on therapy. Am J Gastroenterol 97:1687–1695, 2002
Saribasak H, Salih BA, Yamaoka Y, Sander E: Analysis of Helicobacter pylori genotypes and correlation with clinical outcome in Turkey. J Clin Microbiol 42:1648–1651, 2004
Penston JG, McColl KE: Eradication of Helicobacter pylori: an objective assessment of current therapies. Br J Clin Pharmacol 43:223–243, 1997
Houben MH, van de Beek D, Hensen EF, et al.: Systematic review of Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy–the impact of antimicrobial resistance on eradication rates. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 13:1047–1055, 1999
Guarner J, Herrera-Goepfert R, Mohar A, et al.: Gastric atrophy and extent of intestinal metaplasia in a cohort of Helicobacter pylori-infected patients. Hum Pathol 32:31–35, 2001
Hirschl AM, Brandstatter G, Dragosics B, et al.: Kinetics of specific IgG antibodies for monitoring the effect of anti-Helicobacter pylori chemotherapy. J Infect Dis 168:763–66, 1993
Kosunen TU: Antibody titres in Helicobacter pylori infection: implications in the follow-up of antimicrobial therapy. Ann Med 27:605–607, 1995
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salih, B.A., Abasiyanik, M.F., Saribasak, H. et al. A Follow-up Study on the Effect of Helicobacter pylori Eradication on the Severity of Gastric Histology. Dig Dis Sci 50, 1517–1522 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-2871-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-2871-7