Abstract
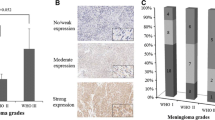
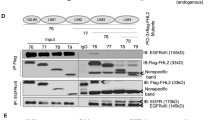
Nucleolin is a multifunctional protein whose expression often correlates with increased cellular proliferation. While the expression of nucleolin is often elevated in numerous cancers, its expression in normal human brain and in astrocytomas has not been previously reported. Using paraffin-embedded sections from normal adult autopsy specimens and glioma resection specimens, we demonstrate that nucleolin expression is limited in the normal human brain specifically to mature neurons, ependymal cells, and granular cells of the dentate gyrus. While astrocytes in the normal human brain do not express nucleolin at significant levels, glioblastoma cell lines and primary human astrocytoma cells exhibit considerable nucleolin expression. Reduction of nucleolin expression through siRNA-mediated knockdown in the U87MG glioblastoma cell line caused a dramatic decrease in cell proliferation and induced cell cycle arrest in vitro. Moreover, conditional siRNA knockdown of nucleolin expression in U87MG intracranial xenografts in nude mice caused dramatic reduction in tumor size. Taken together, these results implicate nucleolin in the regulation of human astrocytoma proliferation in vitro and tumorigenicity in vivo and suggest that nucleolin may represent a potential novel therapeutic target for astrocytomas.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ginisty H, Sicard H, Roger B, Bouvet P (1999) Structure and functions of nucleolin. J Cell Sci 112(Pt 6):761–772
Tuteja R, Tuteja N (1998) Nucleolin: a multifunctional major nucleolar phosphoprotein. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 33(6):407–436. doi:10.1080/10409239891204260
Srivastava M, Pollard HB (1999) Molecular dissection of nucleolin’s role in growth and cell proliferation: new insights. Faseb J 13(14):1911–1922
Borer RA, Lehner CF, Eppenberger HM, Nigg EA (1989) Major nucleolar proteins shuttle between nucleus and cytoplasm. Cell 56(3):379–390
Kleinman HK, Weeks BS, Cannon FB, Sweeney TM, Sephel GC, Clement B, Zain M, Olson MO, Jucker M, Burrous BA (1991) Identification of a 110-kDa nonintegrin cell surface laminin-binding protein which recognizes an A chain neurite-promoting peptide. Arch Biochem Biophys 290(2):320–325
Shi H, Huang Y, Zhou H, Song X, Yuan S, Fu Y, Luo Y (2007) Nucleolin is a receptor that mediates antiangiogenic and antitumor activity of endostatin. Blood 110(8):2899–2906. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-01-064428
Watanabe T, Tsuge H, Imagawa T, Kise D, Hirano K, Beppu M, Takahashi A, Yamaguchi K, Fujiki H, Suganuma M (2010) Nucleolin as cell surface receptor for tumor necrosis factor-alpha inducing protein: a carcinogenic factor of Helicobacter pylori. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136(6):911–921. doi:10.1007/s00432-009-0733-y
Schneider HR, Issinger OG (1988) Nucleolin (C23), a physiological substrate for casein kinase II. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 156(3):1390–1397
Miranda GA, Chokler I, Aguilera RJ (1995) The murine nucleolin protein is an inducible DNA and ATP binding protein which is readily detected in nuclear extracts of lipopolysaccharide-treated splenocytes. Exp Cell Res 217(2):294–308. doi:10.1006/excr.1995.1090
Chen CM, Chiang SY, Yeh NH (1991) Increased stability of nucleolin in proliferating cells by inhibition of its self-cleaving activity. J Biol Chem 266(12):7754–7758
Grinstein E, Du Y, Santourlidis S, Christ J, Uhrberg M, Wernet P (2007) Nucleolin regulates gene expression in CD34-positive hematopoietic cells. J Biol Chem 282(17):12439–12449. doi:10.1074/jbc.M608068200
Khurts S, Masutomi K, Delgermaa L, Arai K, Oishi N, Mizuno H, Hayashi N, Hahn WC, Murakami S (2004) Nucleolin interacts with telomerase. J Biol Chem 279(49):51508–51515. doi:10.1074/jbc.M407643200
Grinstein E, Shan Y, Karawajew L, Snijders PJ, Meijer CJ, Royer HD, Wernet P (2006) Cell cycle-controlled interaction of nucleolin with the retinoblastoma protein and cancerous cell transformation. J Biol Chem 281(31):22223–22235. doi:10.1074/jbc.M513335200
Takagi M, Absalon MJ, McLure KG, Kastan MB (2005) Regulation of p53 translation and induction after DNA damage by ribosomal protein L26 and nucleolin. Cell 123(1):49–63. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.07.034
Soundararajan S, Wang L, Sridharan V, Chen W, Courtenay-Luck N, Jones D, Spicer EK, Fernandes DJ (2009) Plasma membrane nucleolin is a receptor for the anticancer aptamer AS1411 in MV4-11 leukemia cells. Mol Pharmacol 76(5):984–991. doi:10.1124/mol.109.055947
Bates PJ, Laber DA, Miller DM, Thomas SD, Trent JO (2009) Discovery and development of the G-rich oligonucleotide AS1411 as a novel treatment for cancer. Exp Mol Pathol 86(3):151–164. doi:10.1016/j.yexmp.2009.01.004
Ridley L, Rahman R, Brundler MA, Ellison D, Lowe J, Robson K, Prebble E, Luckett I, Gilbertson RJ, Parkes S, Rand V, Coyle B, Grundy RG (2008) Multifactorial analysis of predictors of outcome in pediatric intracranial ependymoma. Neuro Oncol 10(5):675–689. doi:10.1215/15228517-2008-036
Reddy GR, Bhojani MS, McConville P, Moody J, Moffat BA, Hall DE, Kim G, Koo YE, Woolliscroft MJ, Sugai JV, Johnson TD, Philbert MA, Kopelman R, Rehemtulla A, Ross BD (2006) Vascular targeted nanoparticles for imaging and treatment of brain tumors. Clin Cancer Res 12(22):6677–6686
Orringer DA, Koo YE, Chen T, Kim G, Hah HJ, Xu H, Wang S, Keep R, Philbert MA, Kopelman R, Sagher O (2009) In vitro characterization of a targeted, dye-loaded nanodevice for intraoperative tumor delineation. Neurosurgery 64(5):965–971. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000344150.81021.AA discussion 971–962
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, Bonn VE, Hawkins C, Squire J, Dirks PB (2003) Identification of a cancer stem cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res 63(18):5821–5828
Goldhoff P, Warrington NM, Limbrick DD Jr, Hope A, Woerner BM, Jackson E, Perry A, Piwnica-Worms D, Rubin JB (2008) Targeted inhibition of cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase-4 promotes brain tumor regression. Clin Cancer Res 14(23):7717–7725. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0827
Rubin JB, Kung AL, Klein RS, Chan JA, Sun Y, Schmidt K, Kieran MW, Luster AD, Segal RA (2003) A small-molecule antagonist of CXCR4 inhibits intracranial growth of primary brain tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(23):13513–13518. doi:10.1073/pnas.2235846100
Yang L, Jackson E, Woerner BM, Perry A, Piwnica-Worms D, Rubin JB (2007) Blocking CXCR4-mediated cyclic AMP suppression inhibits brain tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Res 67(2):651–658. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2762
Gross S, Piwnica-Worms D (2005) Real-time imaging of ligand-induced IKK activation in intact cells and in living mice. Nat Methods 2(8):607–614. doi:10.1038/nmeth779
Wang GP, Bushman FD (2006) A statistical method for comparing viral growth curves. J Virol Methods 135(1):118–123. doi:10.1016/j.jviromet.2006.02.008
Pontvianne F, Abou-Ellail M, Douet J, Comella P, Matia I, Chandrasekhara C, Debures A, Blevins T, Cooke R, Medina FJ, Tourmente S, Pikaard CS, Saez-Vasquez J (2010) Nucleolin is required for DNA methylation state and the expression of rRNA gene variants in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet 6(11):e1001225. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1001225
Kibbey MC, Johnson B, Petryshyn R, Jucker M, Kleinman HK (1995) A 110-kD nuclear shuttling protein, nucleolin, binds to the neurite-promoting IKVAV site of laminin-1. J Neurosci Res 42(3):314–322. doi:10.1002/jnr.490420305
Chirumamilla S, Sun D, Bullock MR, Colello RJ (2002) Traumatic brain injury induced cell proliferation in the adult mammalian central nervous system. J Neurotrauma 19(6):693–703. doi:10.1089/08977150260139084
Mourmouras V, Cevenini G, Cosci E, Epistolato MC, Biagioli M, Barbagli L, Luzi P, Mannucci S, Miracco C (2009) Nucleolin protein expression in cutaneous melanocytic lesions. J Cutan Pathol 36(6):637–646. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2008.01126.x
Ugrinova I, Monier K, Ivaldi C, Thiry M, Storck S, Mongelard F, Bouvet P (2007) Inactivation of nucleolin leads to nucleolar disruption, cell cycle arrest and defects in centrosome duplication. BMC Mol Biol 8:66. doi:10.1186/1471-2199-8-66
Ritchie C, Doran B, Shah K, Rowlinson-Busza G, Courtenay-Luck N, Jones D (2007) Combination of the aptamer AS1441 with paclitaxel or Ara-C produces synergistic inhibition of cancer cell growth. AACR
Destouches D, El Khoury D, Hamma-Kourbali Y, Krust B, Albanese P, Katsoris P, Guichard G, Briand JP, Courty J, Hovanessian AG (2008) Suppression of tumor growth and angiogenesis by a specific antagonist of the cell-surface expressed nucleolin. PLoS ONE 3(6):e2518
Krust B, El Khoury D, Soundaramourty C, Nondier I, Hovanessian AG (2011) Suppression of tumorigenicity of rhabdoid tumor derived G401 cells by the multivalent HB-19 pseudopeptide that targets surface nucleolin. Biochimie 93(3):426–433. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2010.10.015
Saxena A, Rorie CJ, Dimitrova D, Daniely Y, Borowiec JA (2006) Nucleolin inhibits Hdm2 by multiple pathways leading to p53 stabilization. Oncogene 25(55):7274–7288. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209714
Otake Y, Soundararajan S, Sengupta TK, Kio EA, Smith JC, Pineda-Roman M, Stuart RK, Spicer EK, Fernandes DJ (2007) Overexpression of nucleolin in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells induces stabilization of bcl2 mRNA. Blood 109(7):3069–3075. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-08-043257
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in part by the Children’s Discovery Institute (MC-LI-2009-03R, JRL) and by P50 CA94056 (DPW).
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Precis: This work shows the importance of nucleolin in regulating glioma growth and suggests regulation of nucleolin may serve as a valuable therapeutic target in treatment of gliomas.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Z., Joshi, N., Agarwal, A. et al. Knocking down nucleolin expression in gliomas inhibits tumor growth and induces cell cycle arrest. J Neurooncol 108, 59–67 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-0827-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-0827-2